Data science has changed! Artificial intelligence (AI) does most of the heavy lifting, allowing developers to complete coding-related tasks in a few hours and not a day. What’s even more interesting is the fact that data scientists are among the top nine most in-demand jobs in 2024.
With a median salary of $108,020, a data scientist job is likely a career that will not go away.
Article Roadmap:
- Who Is a Data Scientist?
- What Does a Data Scientist Do?
- Who Can Become a Data Scientist?
- Data Scientist Salary
- Skills Required To Become a Data Scientist
- Industries Hiring Data Scientist
- Conclusion
If you’re a beginner seeking to become a data scientist, this article is ideal for you.
Who Is a Data Scientist
A data scientist is an expert professional who uses mathematical and statistical skills to understand data, read data patterns, identify trends, extract insights from large data volumes and make predictions.
The role of a data scientist involves working with different tools and processes to interpret data and provide actionable recommendations for business decisions.
The lifecycle of a data science project revolves around four stages.
Stage 1: Data Ingestion
The first stage begins with data collection (structured and unstructured data) from relevant sources. In this stage, the data scientist uses methods such as manual entry, real-time data streaming and web scraping from systems and devices.
Data collection sources include structured and unstructured formats – customer data, video, audio, log files, pictures, images, the Internet of Things (IoT), and social media.
Stage 2: Data Storage and Processing
According to the data type, organizations need to consider the data storage systems. The data management team sets the standards around the storage systems and structure. This process facilitates workflows around analytics, deep learning and machine learning models.
In this stage, the data science professional cleans the data, deduplicates it, and transforms it using the ETL (extract, transform and load) integration process. This data preparation process promotes data quality before loading it into data repositories like data lakes and data warehouses.
Stage 3: Data Analysis
Data scientists conduct exploratory data analysis that examines patterns, ranges and value biases within the data. This analysis serves multiple purposes:
- Determine data relevance
- Drive hypothesis generation for a/b testing
These insights are useful and become reliable in driving business decisions for organizations.
Stage 4: Communication
Communication is critical for data scientists. As a data science professional, the professional must have skills to deliver insights in the form of graphs, charts and other data visualization. These professionals must be super skilled in data visualization tools – Python, R, Tableau, etc.
What Does a Data Scientist Do?
Crunching numbers is not all what a data scientist’s job is all about. They must understand business acumen and how to deliver insights to stakeholders.
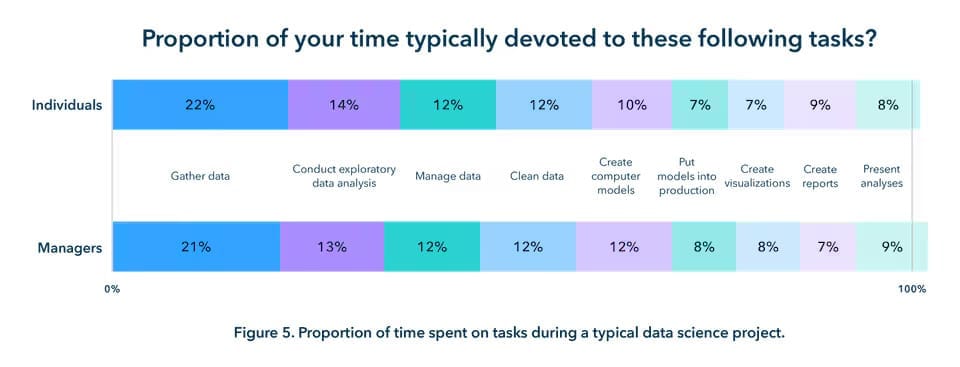
Image Source: SAS Survey
The above illustration demonstrates what a typical project looks like for a data scientist.
Depending upon the organization size and industry type, the day to day roles of a data scientist would include the following.
- Comprehensive knowledge about business acumen to ensure they’re asking the correct questions, identify business pain points and provide informed decisions.
- Apply statistical skills to analyze data.
- Tools and techniques for data preparation and extraction.
- Extract insights using AI, machine learning, deep learning, NLP (natural language processing) and predictive analytics.
- Create data models and algorithms to forecast business outcomes.
- Apply machine learning techniques to improve data and product quality.
- Collaborate with team members, including data architects, business analysts, IT professionals, and data engineers, to discuss solutions.
Who Can Become a Data Scientist?
A data scientist’s career is challenging, and it would be wrong to say that this profession is for everyone. Let us look at some professions (apart from a fresher) that can easily pave the way toward becoming a data scientist.
Data Analysts
A Data analyst can quickly shift their careers and become a data scientist. The work of a data analyst is similar to that of a data scientist. However, a data scientist tends to have a bigger responsibility, and their focus may be more on solving complex problems using data-driven approaches.
- Programming languages include Python, R, C++, Perl and Java.
- SQL databases.
- Machine learning models – K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Linear and Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machines and more.
- Big data platforms – Hadoop, Hive, Pig and Apache Spark.
Business Analysts
As a business analyst, the professional already has domain experience. Shifting from a business analyst to a data scientist career should not be a challenge. However, there are certain skills a business analyst needs to learn.
- In-depth knowledge of tools – Python, R, Django and SAS.
- Knowledge of algorithms – K Means Clustering, Linear and Logistic Regression, Time Series Analysis, NLP and Decision Trees.
- Cloud tools – Azure, GCP and Amazon S3.
- Basic understanding of the Hadoop platform, SQL, NoSQL and MPP databases.
Software Developers
Software developers looking to take their career up a notch can always make a switch. As a developer, you already possess technical skills; all you need to grasp is data science skills – how to crunch data, how to work with different algorithms and solve data challenges.
Additional skills include the following.
- Logic and Linear Programming, Data Parsing and Profiling.
- Expert Systems, Neural Networks and Clustering Algorithms.
- AI and Machine Learning Algorithms.
- Decision Trees and Regression Models.
- Chi-squared Tests, Pearson Correlation and Contingency Tables.
System and Database Administrators
With their prerequisite skills, these professionals can upgrade their profession and become data scientists. Within the organization itself, they can start building their rapport and work with the data science teams.
Data Scientist Salary
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, a data scientist earns a median salary of $108,020 per year and approximately $51.93 per hour. The employment rate is predicted to grow to 36% by 2033 compared to other occupations.
In India, a data scientist’s salary may vary based on multiple factors – industry type, organization size, education, work experience and location. According to Glassdoor, the base pay may vary between ₹8L – ₹20.0 lakh per year.
Skills Required To Become a Data Scientist
Becoming a data scientist requires a solid understanding of mathematics and statistics. Without basic knowledge, acquiring a role as a data scientist can be challenging. Below are a few steps to consider.
Pursue a Degree
Academic credentials prove your ability to tackle data science problems. Though not always required, most organizations still seek candidates having educational qualifications in these fields.
Nearly half of all data scientists hold a bachelor’s degree, while some have earned a master’s degree.
However, considering a degree in mathematics, statistics, and computer science are great foundations for a data science career. If you already have a bachelor’s degree, you can always pursue your master’s and get into data science (not always mandatory). Candidates who already have professional experience can always take up professional certifications to learn additional skills.
Sharpen Relevant Skills
An undergraduate degree equips you with the basic skills required as a data scientist. All you need is to leverage these skills and build proficiency in learning data science tools and techniques. Let’s look at the technical and transferable skills.
Technical Skills
- Python, R and SQL
- Statistics, Probability, Calculus
- Data mining and warehousing
- Machine learning and AI
- Big Data Hadoop and Spark
Transferable Skills
- Communication Skills and Business Acumen
- Problem-Solving
- Creativity
- Analysis
Get Certified
Employers are more likely to hire candidates with credible professional certifications. There are multiple data science certifications available. However, be sure to choose the certification that aligns with your professional goals.
We have listed down some credible certifications to choose from.
- Analytics: Certified Analytics Professional (CAP)
- Google Cloud Technologies: Google Cloud Professional Data Engineer
- Advanced Analytics: SAS (Statistical Analysis System) Certified Data Scientist
- AWS Data Lakes and Analytics: Amazon Web Services (AWS) Certified Data Analytics Specialty
- Microsoft Products: Microsoft Certified
Industries Hiring Data Scientist
Most industries are hiring professionals skilled in data science. As data continues to grow, organizations will consistently seek skilled data scientists to leverage data.
- Healthcare and Life Sciences
- Technology
- Banking and Finance
- Retail and eCommerce
- Public Sector
- Telecom and Media
- Academic Research
- Insurance
Conclusion
Becoming a data scientist is no easy task; it takes significant time and effort. Data science is not just about coding and business acumen. As an aspiring data science professional, it is essential to effectively communicate with business stakeholders and present insights that are clear and accessible to non-data experts.
Related: How To Become a Marketing Analyst
Related: Top 10 AI Leaders To Follow in 2025